In the modern world, technological discoveries and inventions are rapidly increasing. With the new pathways open to many scientific research opportunities, new satellites and machineries are being built each day in the space industry. Though there are many satellites in the market, five of the key satellites have been made clear in this article. They are Electro-Optical (EO), Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), Hyperspectral, Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), and Electronic Intelligence (ELINT).
Electro-Optical (EO) Satellites: Clarity and quality
With the help of optical sensors, electro optical satellites capture high resolution images of the Earth’s surface. They can be both colour coded and monochrome. With their resolution levels, ranging down to sub-metre levels, EO satellites are used for in various industries for urban planning, agriculture planning etc.
The satellites contain multispectral sensors which can capture images of different electromagnetic spectrum. It helps in finding the soil condition, ground water levels. Additionally, due to its precise mapping, EO satellites are used to monitor geographic changes.
LANDSAT, which is run by NASA is one of the longest running satellites since 1972. It is primarily used for environmental research and resource management. EO satellites are a vital tool for observing and understanding our planet, offering precise and comprehensive data that support a wide array of critical applications across different sectors.

Source : Wikipedia – EO MASINT
SAR Satellites: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites are widely known for capturing high resolution images irrespective of the weather conditions or time of the day. SAR satellites use radar waves to create detailed images of the Earth. Unlike optical satellites that rely on sunlight and clear skies, SAR satellites can operate in complete darkness and through cloud cover, smoke, and even dense vegetation. Their ability to provide high resolution images make them stand first for topography visualisation.
SAR satellites are used widely in the fields associated with geology. They monitor sea level, glaciers, and icebergs near the polar regions. They are deeply involved in oceanography. They help in tracking ships, maintain maritime security.
SAR satellites provide critical information during natural disasters. They can map flood extents, assess damage from earthquakes, and monitor volcanic activity, aiding in timely response and recovery efforts.

Source : Digital Geography – CAPELLA SAR
Hyperspectral Satellites: The Spectrum Beyond Vision
Hyperspectral satellites offer photography with colours ranging in the visible spectrum (red, blue, green) of the electromagnetic waves. They can capture data in hundreds of spectral bands. Each material on Earth reflects and absorbs light differently at various wavelengths, creating a unique spectral fingerprint. By identifying the fingerprint, the material can be identified with high precision.
Hyperspectral satellites are widely used in environmental monitoring. This helps the geologists to study the pattern of climate changes. They can measure AQI (Air quality Index), detect sources of contamination etc. It can detect and map mineral deposits by analysing the spectral signatures of different materials. This capability helps geologists and mining companies identify potential mining sites with greater accuracy and efficiency. During natural disasters, hyperspectral satellites provide critical information for response and recovery efforts. New developments in hyperspectral technology have produced more affordable, smaller satellite systems with improved imaging performance. Hyperspectral data is becoming more widely available and applicable because of these advancements. With advancements like real-time data transfer and onboard processing, hyperspectral imaging is becoming increasingly useful for a greater variety of applications by facilitating quicker and more effective data analysis.

Source : TIME – Hyperspectral images.
SIGINT Satellites
SIGINT satellites (Signals Intelligence) satellites is a major advancement in the modern development. Specialised spacecraft known as SIGINT satellites are made to intercept and gather electronic signals from a range of sources. Radio broadcasts, cell phone conversations, satellite communications, and other electromagnetic emissions can all be considered examples of these signals. SIGINT satellites gather and examine these signals to give precise information about the whereabouts and goals of possible enemies as well as the overall state of communication.
The satellites are equipped with antennas which can detect frequencies of various wavelength. These observe the characteristics and monitor their nature. The data is then transmitted to the ground station.
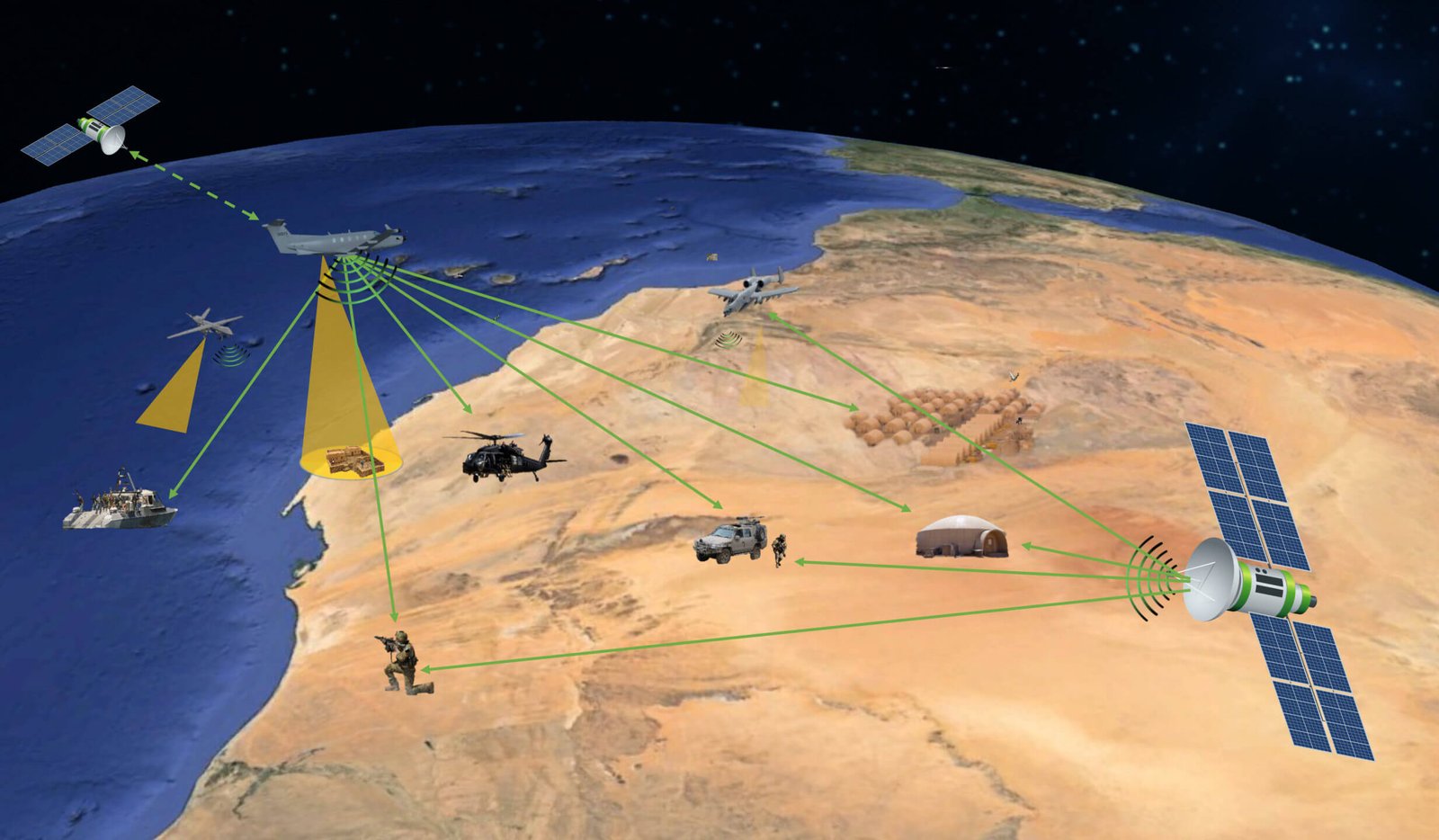
Source : MAG Aerospace – electronic warfare using SIGINT
There are two primary types of SIGINT
- Communication Intelligence (COMINT)
- Electronics Intelligence (ELINT)
Intercepting electronic signals not meant for communication, such radar emissions and other signals used for military purposes, is known as electronic signal intelligence, or ELINT.
These types of satellites are widely used in the modern space and its technological developments.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ)
- What is the purpose of SIGINT satellites?
SIGINT is intelligence derived from electronic signals and systems used by foreign targets, such as communications systems, radars, and weapons systems that provides a vital window for our nation into foreign adversaries’ capabilities, actions, and intentions.
2. What is the principle of SAR?
SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars.